Discovery of 2,6-Dihalopurines as Stomata Opening Inhibitors: Implication of an LRX-Mediated H+-ATPase Phosphorylation Pathway
Ayaka Ueda, Yusuke Aihara, Shinya Sato, Keiko Kano, Emi Mishiro-Sato, Hiroyuki Kitano, Ayato Sato, Kazuhiro J. Fujimoto*, Takeshi Yanai, Kazuma Amaike*, Toshinori Kinoshita*, and Kenichiro Itami.
ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, accepted, DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00771
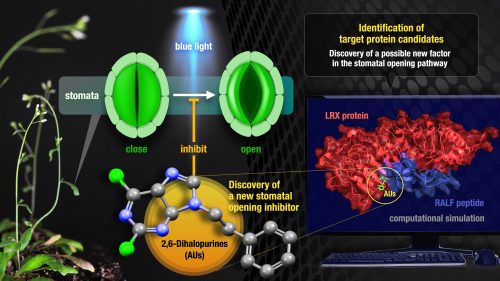
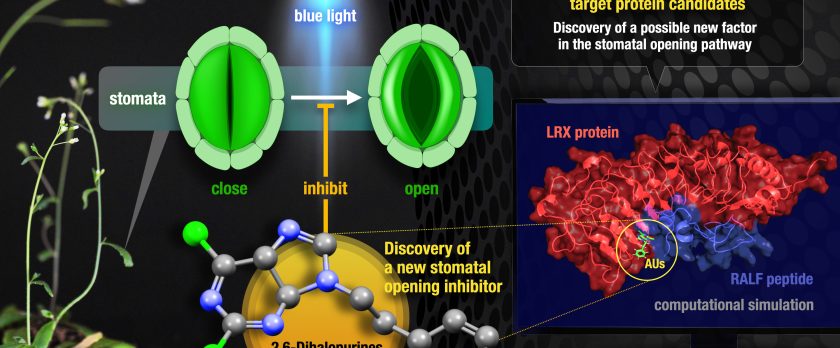
Stomata are pores in the leaf epidermis of plants and their opening and closing regulate gas exchange and water transpiration. Stomatal movements play key roles in both plant growth and stress responses. In recent years, small molecules regulating stomatal movements have been used as a powerful tool in mechanistic studies, as well as key players for agricultural applications. Therefore, the development of new molecules regulating stomatal movement and the elucidation of their mechanisms have attracted much attention. We herein describe the discovery of 2,6-dihalopurines, AUs, as a new stomatal opening inhibitor, and their mechanistic study. Based on biological assays, AUs may involve in the pathway related with plasma membrane H+-ATPase phosphorylation. In addition, we identified leucine-rich repeat extensin proteins (LRXs), LRX3, LRX4 and LRX5 as well as RALF, as target protein candidates of AUs by affinity based pull down assay and molecular dynamics simulation. The mechanism of stomatal movement related with the LRXs–RALF is an unexplored pathway, and therefore further studies may lead to the discovery of new signaling pathways and regulatory factors in the stomatal movement.