

Guillaume Povie, Yasutomo Segawa, Taishi Nishihara, Yuhei Miyauchi, and Kenichiro Itami
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b06842
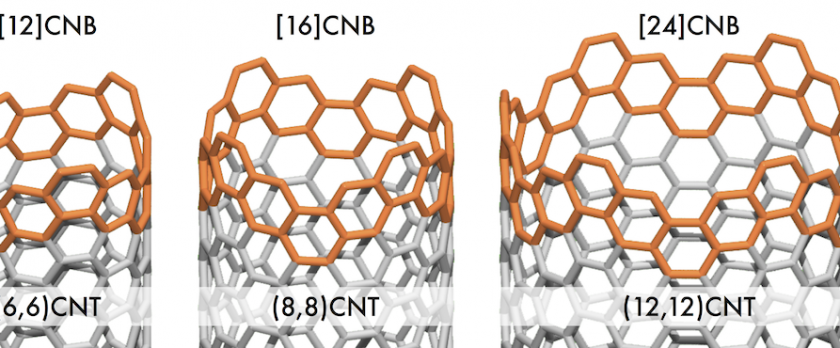
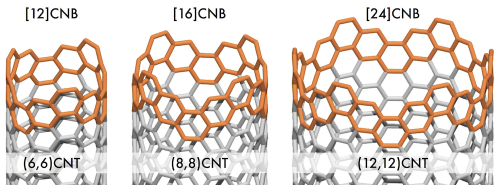 The synthesis and X-ray crystal structure of the first member of the carbon nanobelt family is reported. [12]carbon nanobelt ([12]CNB) was originally obtained from a nickel-mediated reductive coupling reaction of a dodecabrominated macrocyclic precursor, albeit only in 1% yield. The present article reports on the development of this synthetic strategy and its extension to the preparation of the [16] and [24]CNB analogues. In particular, our extensive investigations on the final belt-forming, nickel-mediated reaction led to the development of a new ligand system that provides [12]CNB in up to 7% yield, contributing the commercialization of [12]CNB. The belt structures of [12], [16], and [24]CNB were characterized by NMR, UV-vis, and Raman spectroscopy as well as mass spectrometry and X-ray crystallography. The fluorescence of the CNBs in solution displayed a remarkable dependence on the ring size, ranging from a broad red emission ([12]CNB) to a narrow-band blue emission ([24]CNB), while both features are observed for [16]CNB.
The synthesis and X-ray crystal structure of the first member of the carbon nanobelt family is reported. [12]carbon nanobelt ([12]CNB) was originally obtained from a nickel-mediated reductive coupling reaction of a dodecabrominated macrocyclic precursor, albeit only in 1% yield. The present article reports on the development of this synthetic strategy and its extension to the preparation of the [16] and [24]CNB analogues. In particular, our extensive investigations on the final belt-forming, nickel-mediated reaction led to the development of a new ligand system that provides [12]CNB in up to 7% yield, contributing the commercialization of [12]CNB. The belt structures of [12], [16], and [24]CNB were characterized by NMR, UV-vis, and Raman spectroscopy as well as mass spectrometry and X-ray crystallography. The fluorescence of the CNBs in solution displayed a remarkable dependence on the ring size, ranging from a broad red emission ([12]CNB) to a narrow-band blue emission ([24]CNB), while both features are observed for [16]CNB.